Amazon Athena
Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data directly in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) using standard SQL. With a few actions in the AWS Management Console, you can point Athena at your data stored in Amazon S3 and begin using standard SQL to run ad-hoc queries and get results in seconds.
Source: AWS
Accessing Amazon Athena
You can access the AWS console at aws.services.analytical-platform.service.justice.gov.uk. You may need to login with GitHub and go through two-factor authentication.
To access Athena, select Services, then Athena.
This will bring you to the Athena query editor. Here, you can:
- access and create databases and tables
- write, run and save queries
- view and download query outputs to your local computer
Athena Access Issue
Some users may find when first running a query in the Athena editor, that they get an error similar to:
Access denied when writing output to url: s3://<bucket_name>/<file_name.csv>.
Please ensure you are allowed to access the S3 bucket.
If you are encrypting query results with KMS key, please ensure you are allowed to access your KMS key
A fix for this error can be found here.
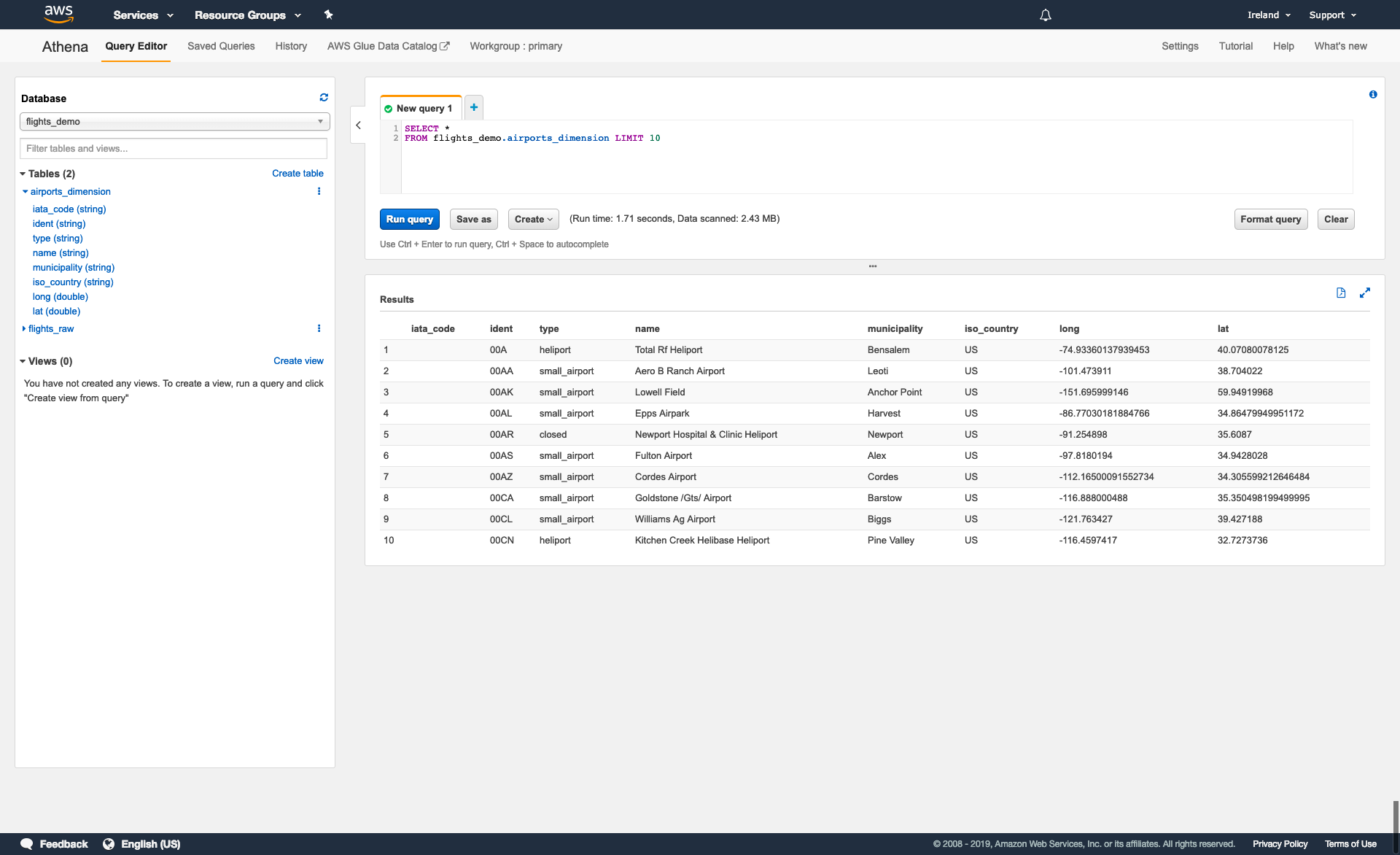
Previewing tables
In many cases, it may be useful to preview a table to get a better understanding of its structure and contents.
To preview a table, select a database using the dropdown menu and find the object you want to preview either directly from the list or using the Filter table and views… search bar.
You can view the name and type of each column in a table by selecting the blue arrow to the left of the object name.
To run a query to preview a table, select the three dots (⋮) to the right of the object name and select Preview table. This will run the following query that selects all columns from the table and returns 10 rows from the output:
SELECT *
FROM database_name.table_name
LIMIT 10;
Working with tables
You can create, update and delete tables using the code in the SQL section, however, you must also specify the storage format and location of the table in S3.
You can also use Rstudio, JupyterLab and the Athena UI. In particular, the Athena UI allows you to create tables directly from data stored in S3 or by using the AWS Glue Crawler. This guidance does not cover use of the AWS Glue Crawler.
Using RStudio
The Analytical platform hosts a number of analytical coding environments. For those experienced in R, you can query Athena using the RStudio tool.
To execute Athena queries, you can use the data engineering team maintained package dbtools. This package uses the Python package pydbtools under the hood and works alongside user IAM policies on the platform. It is also significantly faster than using database drivers provided by Amazon.
Follow the setup guidance to get started. The quickstart guidance here provides detailed examples for creating, querying and deleting tables.
You can also use Rdbtools. This is an analytical platform community maintained package which has some additional functionality that dbtools does not. It can be used with the understanding that if the package requires fixing or updating, it is the responsibility of those using the package to do so.
Using JupyterLab
Another analytical tool available on the platform is JupyterLab, which you can use to query Athena data via Python scripts.
To do this, install the pydbtools package. This is a wrapper for awswrangler that which presets/defines some of the input parameters to the athena module functions to align with our platform setup.
You can perform advanced tasks such as utilising temporary tables, creating and deleting. See the quickstart guide for more details.
Using the Athena UI
Create a table
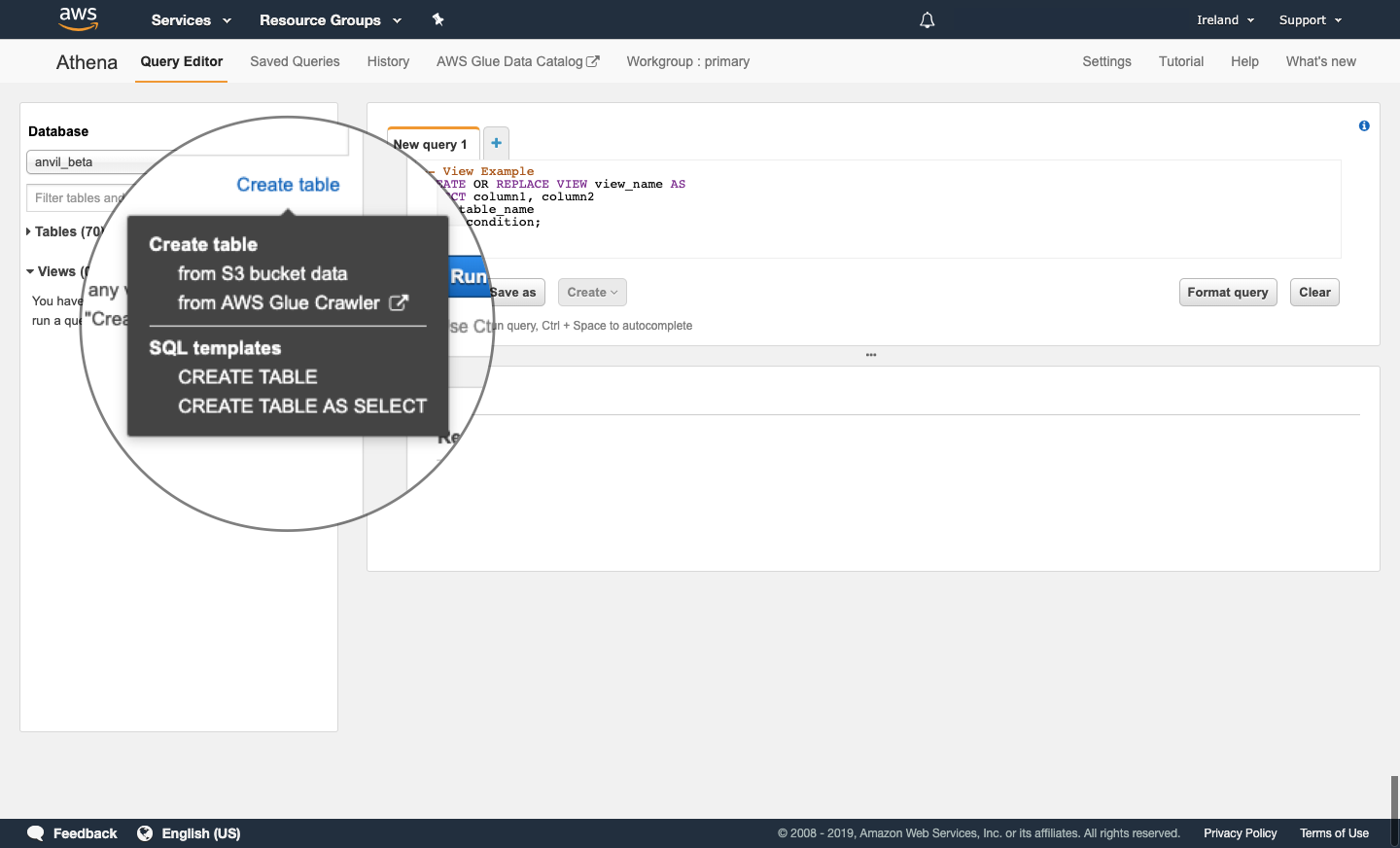
Create a table using drop-down menus
Selecting Create table in the database window brings up a menu list with the following options:
- Create table
- From S3 bucket data
- from AWS Glue Crawler
- SQL templates
- CREATE TABLE
- CREATE TABLE AS SELECT
Selecting CREATE TABLE or CREATE TABLE AS SELECT generates an example query that you can edit to create a new table. These example queries are of the same form as those described in the previous section.
Selecting from S3 bucket data will open a new window that guides you through four steps to create a new table from data in S3:
- Select which database to store your table in, input a name for your table and input the S3 path to the data from which you want to make the table. The S3 path should be of the form
s3://bucket/folder/. - Select the format of the input data. You may also have to complete additional fields depending on the format of the input data.
- Input the name and data type of each column in the table. When adding a large number of columns, it may be easier to use the Bulk add columns option.
- Select whether you want to partition the data in the table. This step is optional.
Create a table using SQL code
If using code to create a table in Athena, you must also specify the storage format and location of the table in S3.
If creating a table from existing data, you can specify this information using the WITH statement.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS database_1.table_1
WITH (format = 'format', external_location = 'location') AS
SELECT *
FROM database_name.table_name;
Here, format can be any of the following:
ORCPARQUETAVROJSONTEXTFILE
If format is not specified, PARQUET is used by default.
Additionally, location is the S3 path where you would like to store the table, for example, s3://alpha-everyone.
There are several other parameters that you can specify. Information on these parameters can be found in the Athena documentation.
If you are creating a new table, you can specify the storage format using the STORED AS statement and the storage location using the LOCATION statement.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS table_1 AS (
column_name1 column_type1,
column_name2 column_type2,
...
)
STORED AS 'format'
LOCATION 'location';
Here, format and location are the same as above.
Delete a table
To delete a table using the Athena UI, select the three dots (⋮) next to the name of the table you want to delete and select Delete table.
Run a query
To create and run a new query:
- Select the plus (+) tab above the editor window.
- Write your code in the editor window (or copy and paste from another editor).
- Select Run query.
Progress information, including the estimated time elapsed will be displayed in the results window while the query is being processed.
Once the query has been completed, the output will be displayed in the results window.
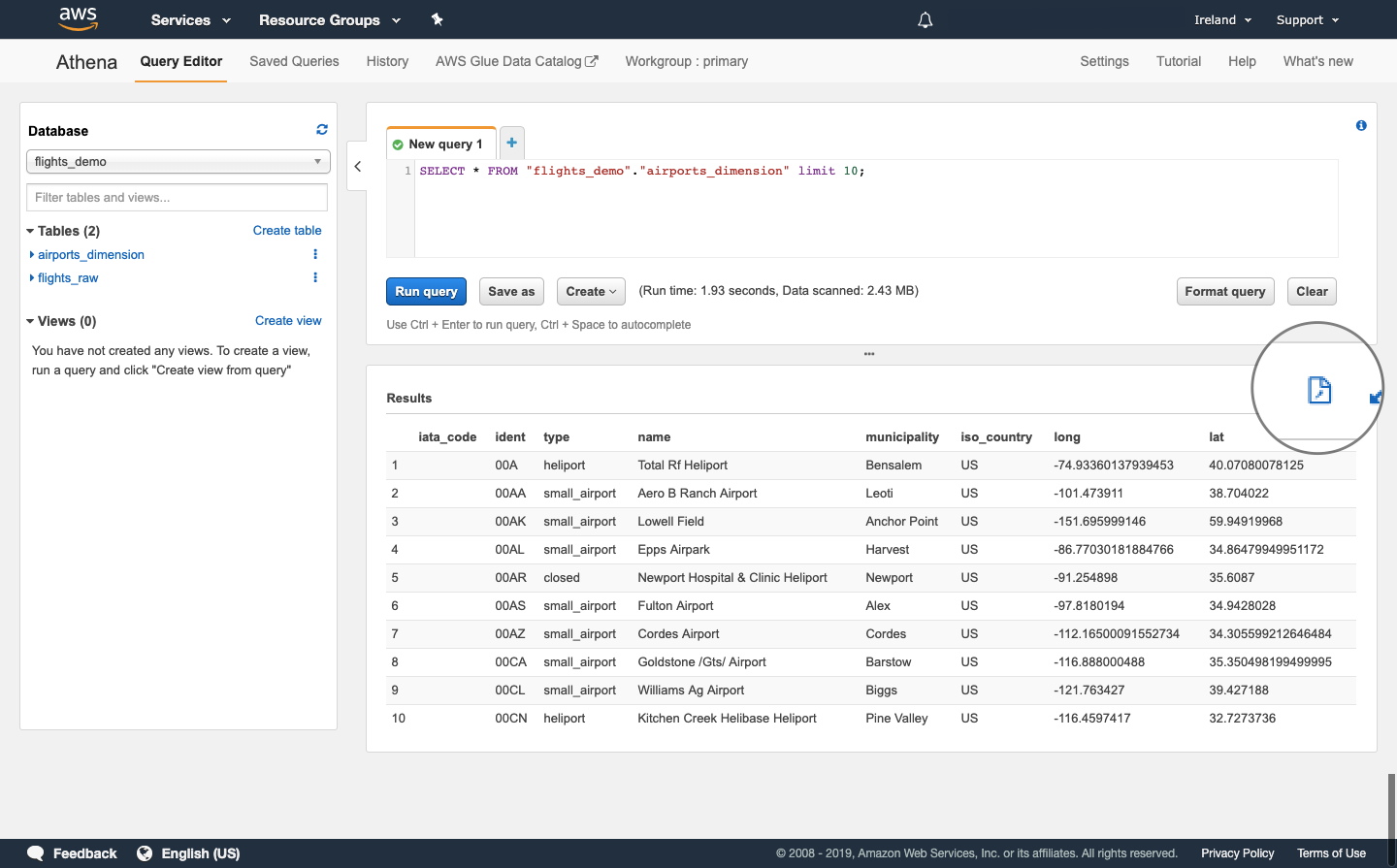
Download query outputs
When you have run a query, you can download the output to your local computer as a CSV file.
To download the output, select the page icon above the results table.
SQL resources
You might find the SQL Training repository useful. This training is for using SQL (Athena) with the Analytical Platform.
SQL (pronounced ‘S-Q-L’ or ‘sequel’) is a programming language used to access and manipulate databases. There are several versions of SQL that share a common framework but can have different syntax and functionality. The version of SQL used by Amazon Athena is based on Presto 0.217.